Introduction:
The internet has undergone a remarkable transformation since its inception. From the early days of static web pages to today’s dynamic and interactive online experiences, we have witnessed the evolution of the World Wide Web. In this blog post, we will delve into the key characteristics and differences between Web1, Web2, and the emerging concept of Web3. Let’s explore how each iteration has shaped the digital landscape and what lies ahead for the future of the internet.
Web1: The Birth of the Internet:
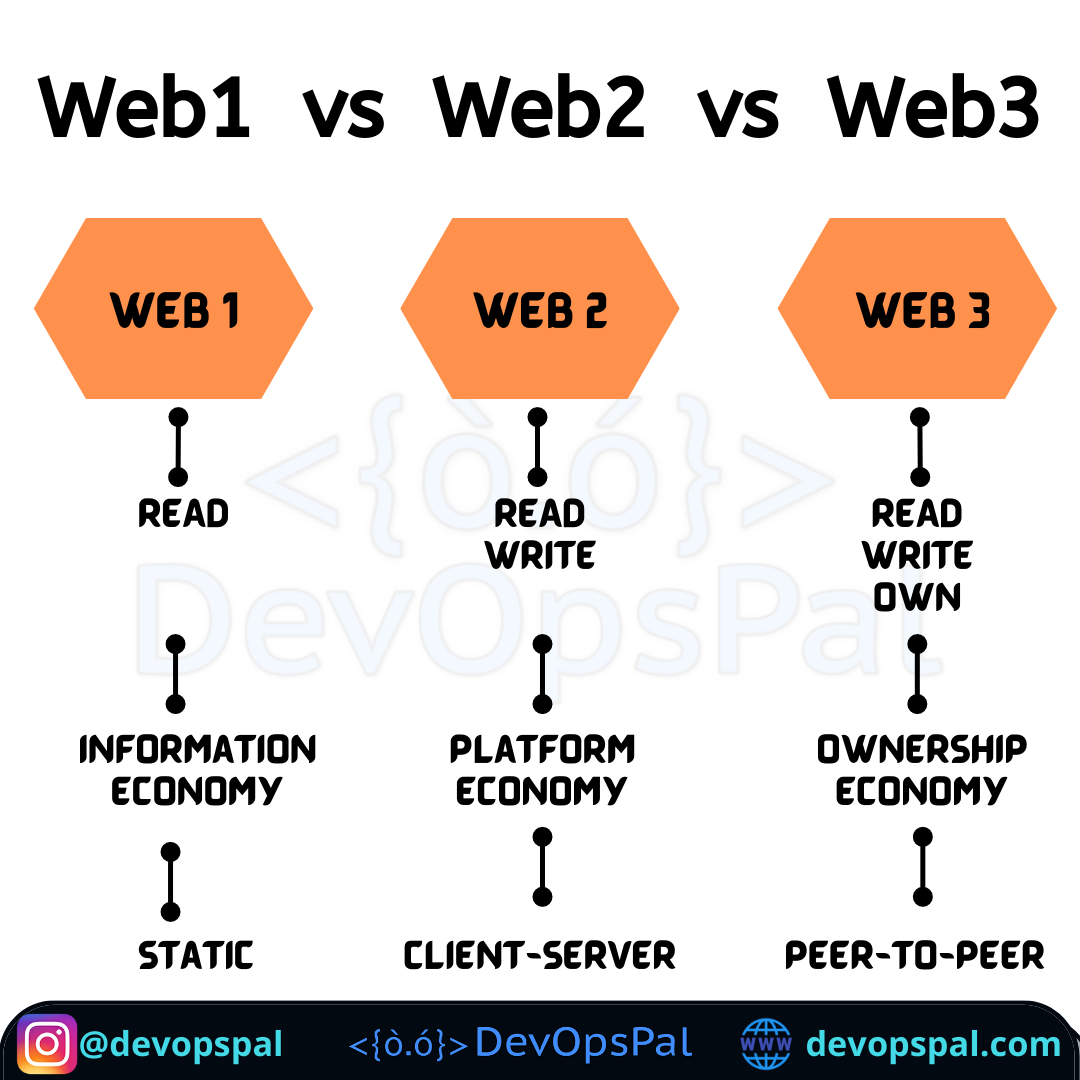
Web1, also known as the “read-only” web, represents the initial stage of the World Wide Web. It emerged in the late 1980s and gained popularity in the 1990s. Web1 was primarily characterized by static websites that offered limited interactivity and focused on the dissemination of information. Users could browse websites, access text-based content, and follow hyperlinks to navigate across different pages. However, the content was predominantly one-way, with users acting as passive consumers.
Web2: The Rise of Interactivity and User-Generated Content:
Web2, often referred to as the “read-write” web, marks a significant shift in the online landscape. It emerged in the early 2000s and continues to dominate the internet today. Web2 introduced dynamic web pages, interactive applications, and user-generated content, empowering individuals to actively participate and contribute. Social media platforms, blogs, forums, and video-sharing websites exemplify the essence of Web2, fostering user engagement, collaboration, and information sharing. Web2 revolutionized online communication, enabling real-time interactions, personalized experiences, and the democratization of content creation.
Web3: The Promise of Decentralization and Web of Trust:
Web3 is an evolving concept that aims to address the limitations of its predecessors by leveraging emerging technologies such as blockchain, decentralized networks, and smart contracts. It envisions a more decentralized, secure, and transparent internet. Web3 shifts the focus from centralized entities controlling user data and online interactions to a distributed architecture where users have greater control over their digital assets and identities.
One of the core principles of Web3 is the concept of trustlessness. Through blockchain technology, Web3 aims to establish trust in a decentralized manner, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements written on the blockchain, enable secure and transparent transactions without relying on a central authority.
Moreover, Web3 fosters the concept of digital ownership, enabling users to have true ownership of their data, creative works, and digital assets. This ownership is facilitated by non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which provide a unique digital representation of tangible or intangible items.
The Potential of Web3:
Web3 holds vast potential for various industries, including finance, healthcare, supply chain management, and more. It opens up new opportunities for decentralized applications (dApps) that operate on peer-to-peer networks, promoting greater privacy, security, and autonomy.
Furthermore, Web3 is expected to transform the creator economy by enabling more direct connections between creators and their audience. With decentralized marketplaces, creators can monetize their work without relying on intermediaries, ensuring fair compensation and more control over their creative endeavors.
Conclusion:
The internet has come a long way since its inception, evolving from the static and one-way Web1 to the interactive and user-driven Web2. Now, with the emergence of Web3, we are witnessing a paradigm shift towards decentralization, trustlessness, and user empowerment.
While Web3 is still in its early stages and faces technical and adoption challenges, its potential to reshape the internet is undeniably promising. As we embrace the possibilities of blockchain, decentralized networks, and digital ownership, we are embarking on a new era where individuals have more control over their digital lives, data privacy is enhanced, and trust is established through transparent and verifiable systems.
However, the transition to Web3 is not without obstacles. Technical scalability, usability, and regulatory considerations are among the challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. Additionally, educating users about the benefits and potential risks of Web3 is crucial to foster understanding and acceptance.
As the concept of Web3 continues to evolve, it is essential for developers, entrepreneurs, policymakers, and users to actively engage in its development and shape its trajectory. Collaboration and innovation will be key to unlocking the full potential of Web3 and creating an internet that aligns with the principles of decentralization, privacy, and user empowerment.
In conclusion, the evolution from Web1 to Web2 and now to Web3 represents a remarkable transformation of the internet. Each iteration has brought new possibilities, reshaped online interactions, and empowered users in different ways. Web3, with its focus on decentralization, trustlessness, and digital ownership, promises to revolutionize industries, redefine the creator economy, and establish a more secure and transparent internet ecosystem. While there are challenges to overcome, the vision of Web3 holds immense potential for a future where individuals have greater control over their digital lives and the internet becomes a more inclusive and equitable space.