Given a 2D grid of size m x n and an integer k. You need to shift the grid k times.
In one shift operation:
- Element at
grid[i][j]moves togrid[i][j + 1]. - Element at
grid[i][n - 1]moves togrid[i + 1][0]. - Element at
grid[m - 1][n - 1]moves togrid[0][0].
Return the 2D grid after applying shift operation k times.
Example 1:
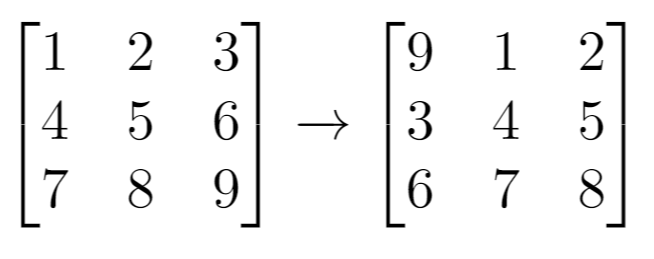
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 1
Output: [[9,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]]
Example 2:
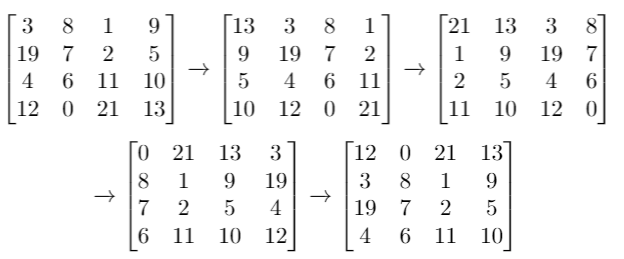
Input: grid = [[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10],[12,0,21,13]], k = 4
Output: [[12,0,21,13],[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10]]
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 9
Output: [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> shiftGrid(int[][] grid, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> gridList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
int rows = grid.length;
int cols = grid[0].length;
if(k==0){
for(int i=0;i<rows;i++){
List<Integer> g = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int j=0;j<cols;j++){
g.add(grid[i][j]);
}
gridList.add(g);
}
}else{
for(int a=0;a<k;a++){
int start = grid[0][0];
int end = grid[rows-1][cols-1];
int nextStart = -10000;
gridList.clear();
for(int i=0;i<rows;i++){
List<Integer> g = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int j=0;j<cols;j++){
if(i==0 && j==0){
g.add(end);
if(j==cols-1) nextStart = grid[i][j];
}
else if(j!=0 && j==cols-1) {
g.add(grid[i][j-1]);
nextStart = grid[i][j];
}
else if(j==0){
g.add(nextStart);
if(j==cols-1) nextStart = grid[i][j];
}
else{
g.add(grid[i][j-1]);
}
}
gridList.add(g);
}
for(int z=0;z<gridList.size();z++){
List<Integer> temp = gridList.get(z);
int[] arr = temp.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
grid[z]=arr;
}
}}
return gridList;
}
}