Given a binary tree, each node has value 0 or 1. Each root-to-leaf path represents a binary number starting with the most significant bit. For example, if the path is 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1, then this could represent 01101 in binary, which is 13.
For all leaves in the tree, consider the numbers represented by the path from the root to that leaf.
Return the sum of these numbers.
Example 1:
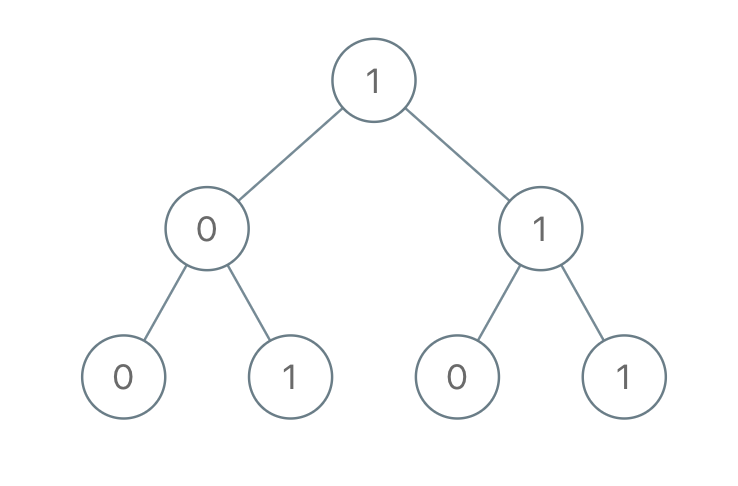
Input: [1,0,1,0,1,0,1] Output: 22 Explanation: (100) + (101) + (110) + (111) = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 22
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<String> numList = new ArrayList<String>();
public int sumRootToLeaf(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode node = root;
String num = "";
int total = 0;
getNum(num, node);
//System.out.println(numList);
for(String n : numList){
int s = Integer.parseInt(n,2);
total = total+s;
}
return total;
}
public void getNum(String rootStr, TreeNode node){
if(node.left !=null) {
getNum(rootStr+node.val,node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
getNum(rootStr+node.val,node.right);
}
if(node.right == null && node.left == null){
rootStr = rootStr+node.val;
numList.add(rootStr);
}
}
}